JAM3 / JAM-C (32-241, His-tag) Human Protein
CAT#: AR50547PU-S
JAM3 / JAM-C (32-241, His-tag) human recombinant protein, 20 µg
Size: 100 ug
|
Need it in bulk or customized? Get a free quote |
CNY 8,900.00
货期*
详询
规格
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MGSMVNLKSS NRTPVVQEFE SVELSCIITD SQTSDPRIEW KKIQDEQTTY VFFDNKIQGD LAGRAEILGK TSLKIWNVTR RDSALYRCEV VARNDRKEID EIVIELTVQV KPVTPVCRVP KAVPVGKMAT LHCQESEGHP RPHYSWYRND VPLPTDSRAN PRFRNSSFHL NSETGTLVFT AVHKDDSGQY YCIASNDAGS ARCEEQEMEV YDLN
|
| Tag | His-tag |
| Predicted MW | 26 kDa |
| Concentration | lot specific |
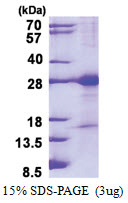
| Purity | >90% by SDS - PAGE |
| Buffer | Presentation State: Purified State: Liquid purified protein Buffer System: 20 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0) containing 0.2M NaCl, 50% glycerol, 2 mM EDTA, 5 mM DTT |
| Preparation | Liquid purified protein |
| Protein Description | Recombinant human JAM3 protein, fused to His-tag at N-terminus, was expressed in E.coli and purified by using conventional chromatography techniques. |
| Storage | Store undiluted at 2-8°C for one week or (in aliquots) at -20°C to -80°C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_001192258 |
| Locus ID | 83700 |
| UniProt ID | Q9BX67 |
| Cytogenetics | 11q25 |
| Synonyms | JAM-2; JAM-3; JAM-C; JAMC |
| Summary | Tight junctions represent one mode of cell-to-cell adhesion in epithelial or endothelial cell sheets, forming continuous seals around cells and serving as a physical barrier to prevent solutes and water from passing freely through the paracellular space. The protein encoded by this immunoglobulin superfamily gene member is localized in the tight junctions between high endothelial cells. Unlike other proteins in this family, the this protein is unable to adhere to leukocyte cell lines and only forms weak homotypic interactions. The encoded protein is a member of the junctional adhesion molecule protein family and acts as a receptor for another member of this family. A mutation in an intron of this gene is associated with hemorrhagic destruction of the brain, subependymal calcification, and congenital cataracts. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, Apr 2011] |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Transmembrane |
| Protein Pathways | Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs), Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection, Leukocyte transendothelial migration, Tight junction |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Customer
Reviews
Loading...


 United States
United States
 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China