SIAH1 (90-282, His-tag) Human Protein
CAT#: AR50493PU-N
SIAH1 (90-282, His-tag) human recombinant protein, 0.25 mg
Size: 50 ug
|
Need it in bulk or customized? Get a free quote |
CNY 17,930.00
货期*
详询
规格
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MGSVANSVLF PCKYASSGCE ITLPHTEKAD HEELCEFRPY SCPCPGASCK WQGSLDAVMP HLMHQHKSIT TLQGEDIVFL ATDINLPGAV DWVMMQSCFG FHFMLVLEKQ EKYDGHQQFF AIVQLIGTRK QAENFAYRLE LNGHRRRLTW EATPRSIHEG IATAIMNSDC LVFDTSIAQL FAENGNLGIN VTISMC
|
| Tag | His-tag |
| Predicted MW | 24.1 kDa |
| Concentration | lot specific |
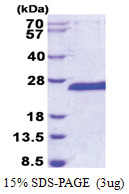
| Purity | >95% by SDS - PAGE |
| Buffer | Presentation State: Purified State: Liquid purified protein Buffer System: 20 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0) containing 0.1M NaCl, 40% glycerol, 1 mM DTT |
| Preparation | Liquid purified protein |
| Protein Description | Recombinant human SIAH1 protein, fused to His-tag at N-terminus, was expressed in E.coli and purified by using conventional chromatography techniques. |
| Storage | Store undiluted at 2-8°C for one week or (in aliquots) at -20°C to -80°C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_001006611 |
| Locus ID | 6477 |
| UniProt ID | Q8IUQ4 |
| Cytogenetics | 16q12.1 |
| Synonyms | BURHAS; SIAH1A |
| Summary | This gene encodes a protein that is a member of the seven in absentia homolog (SIAH) family. The protein is an E3 ligase and is involved in ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation of specific proteins. The activity of this ubiquitin ligase has been implicated in the development of certain forms of Parkinson's disease, the regulation of the cellular response to hypoxia and induction of apoptosis. Alternative splicing results in several additional transcript variants, some encoding different isoforms and others that have not been fully characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome |
| Protein Pathways | p53 signaling pathway, Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis, Wnt signaling pathway |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Customer
Reviews
Loading...


 United States
United States
 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China